Solid State Drives (SSDs) have become a popular choice for storage due to their speed and reliability. However, users must consider one essential factor when purchasing an SSD: the Total Bytes Written (TBW) rating. Understanding SSD TBW, checking it regularly, and monitoring it can help users extend the lifespan of their drive and ensure optimal performance. This article will delve into the importance of SSD Total Bytes Written and how to monitor it effectively.
What is SSD TBW?
Manufacturers grade their drives based on three main characteristics: total bytes written (TBW), drive writes per day, and drive capacity (DWPD). Total Bytes Written is a metric used to measure an SSD’s endurance. It represents the total amount of data that can be written to the drive before it is likely to fail.
TBW, typically measured in terabytes (TB), is a statistic for SSD storage devices that tells you how many terabytes you may write to the drive during its warranty term before the memory cells inside it begin to deteriorate. Thus, the potential for data loss and, eventually, drive failure increases. Essentially, the TBW rating estimates how much data can be written to the drive over its lifespan.
When purchasing an SSD, the Total Bytes Written metrics, price, and capacities should be considered. Purchasing an SSD drive with a high TBW will ensure a longer life than a much lower amount.
How to Check SSD Total Bytes Written
Most SSD manufacturers provide software tools that allow users to monitor the health of their drives, including the TBW rating, and are relatively straightforward. These tools can display information such as the amount of data that has been written to the drive so far, the remaining TBW, and the estimated lifespan based on current usage patterns.
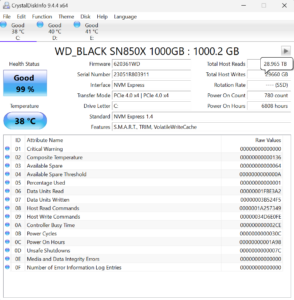
You can also use a third-party tool, CrystalDiskInfo, to check TBW on SSD. The program can be used on Windows 10 or 11, 32-bit or 64-bit. It employs the Self-Monitoring, Analyzing, and Reporting Technology or S.M.A.R.T. method.
Use the following steps to check the SSD TBW using CrystalDiskInfo:
- Download and install CrystalDiskInfo on your computer and run it.
- Once opened, wait for the utility to detect all of your drives.
- Once loaded, select the SSD you like to check in the top row. You can scroll left and right or click on Disk and select the drive you want to check.
- Look for the box that reads Total Host Writes in the utility’s top-right area (pictured). You can also hover your mouse pointer over the number to see a TB reading. This is your drive’s current TBW figure.
Samsung Magician, Western Digital Dashboard, and Hard Disk Sentinel are also good third-party tools for checking SSD health.
Regularly checking your SSD’s TBW can help you monitor its health and make informed decisions about data storage and usage.
Importance of Monitoring TBW
Monitoring your SSD’s TBW is crucial for maintaining its performance and reliability. By keeping track of the amount of data written to the drive, you can anticipate when it may be reaching its endurance limits and start planning for a replacement. Exceeding the TBW rating can lead to data loss and drive failure, so it is essential to monitor your SSD’s health proactively.
Extending SSD Lifespan
Several steps can extend the lifespan of your SSD and maximize its performance. One key factor is to minimize unnecessary write operations by optimizing settings and avoiding excessive data transfers. Additionally, regularly updating firmware and performing TRIM operations can help maintain the health of the NAND flash memory cells. By taking these precautions and monitoring your SSD’s TBW, you can ensure your drive lasts years.

